
Executive Summary
Thailand’s pharmaceutical retail market represents a compelling exit opportunity for pharmacy owners, with the sector projected to reach THB 175.4 billion in 2025 and maintain a robust 4.7% CAGR through 2030 (Thailand Board of Investment, 2025). The market’s fundamental drivers—an aging population (13.07% aged 65+) and growing medical tourism (2.86 million international patients in 2023)—create sustained demand for pharmaceutical services (Expert Market Research, 2025).
Our comprehensive analysis reveals significant valuation disparities between owner-managed sales and professionally guided transactions. Pharmacy businesses using specialized M&A advisors achieve 15-25% higher valuations and demonstrate 4× higher transaction completion rates compared to self-managed sales. The consolidation window is narrowing as organized chains expand market share from 50% to an anticipated 65% by 2027.
This strategic framework outlines the critical six-stage sale process, quantified valuation benchmarks, and specific value-enhancement strategies that can increase EBITDA multiples from 2-4× to 8-10× for optimally positioned assets. Max Solutions, with integrated M&A, legal, and accounting services through Tanormsak Law Firm’s 50+ years of expertise, provides the specialized guidance essential for navigating Thailand’s complex pharmacy M&A landscape.
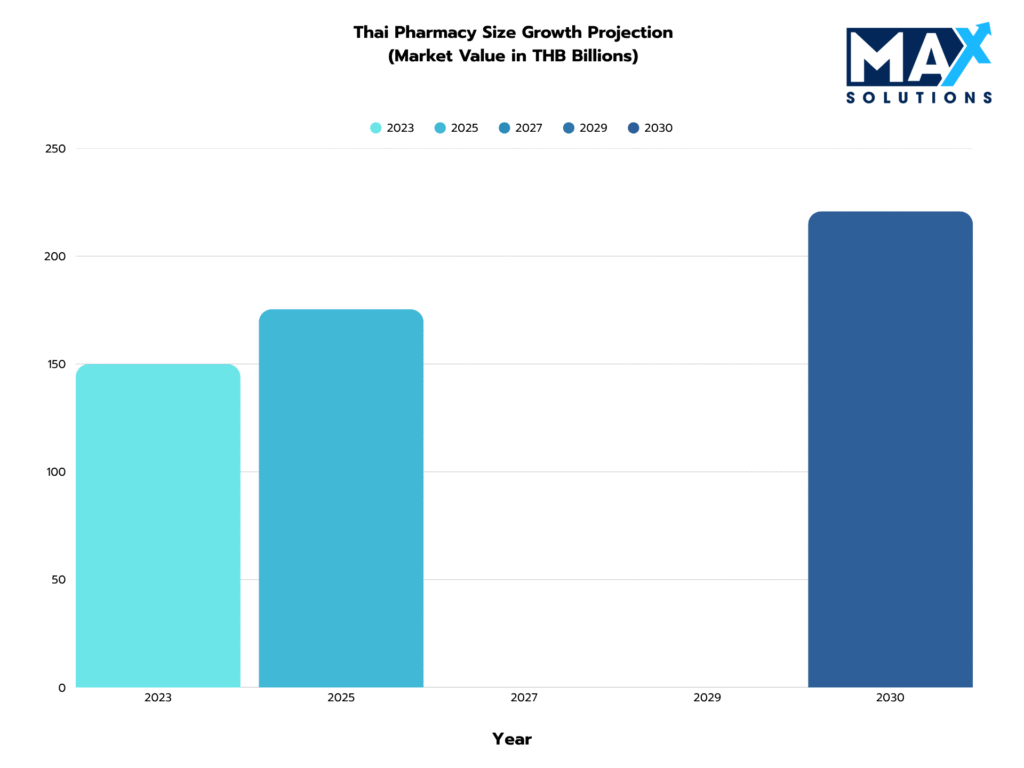
Figure 1: Thai Retail Pharmaceutical Market Growth (THB), 2022-2030E
Introduction
The Thai pharmacy sector stands at a critical inflection point. With over 20,516 pharmacy locations nationwide—80% independently owned—the market faces unprecedented consolidation pressure (Ministry of Public Health, 2025). Major chains including Watson’s (700+ stores), Boots (300+ stores), and emerging players like Fascino (targeting 305 stores by 2026) are aggressively expanding through acquisition and organic growth.
For independent pharmacy owners, this environment presents both opportunity and urgency. Bangkok alone generates 40% of total pharmaceutical retail sales (approximately THB 70-80 billion annually), while regulatory changes including Good Pharmacy Practice (GPP) requirements and Drug Act 2019 implementation create barriers for smaller operators.
The complexity of pharmacy M&A transactions—involving pharmaceutical licenses, GPP compliance, inventory valuation, and Foreign Business Act (FBA) restrictions—demands specialized expertise. Self-managed sales frequently encounter valuation gaps, regulatory hurdles, and transaction failures that professional advisory can prevent.
Valuation Landscape
Pharmacy business valuations in Thailand employ three primary methodologies: EBITDA multiples, revenue multiples, and asset-based approaches. Our analysis of recent transaction data reveals distinct valuation patterns across company size segments, with significant variations based on geographic location client diversification, and operational sophistication.
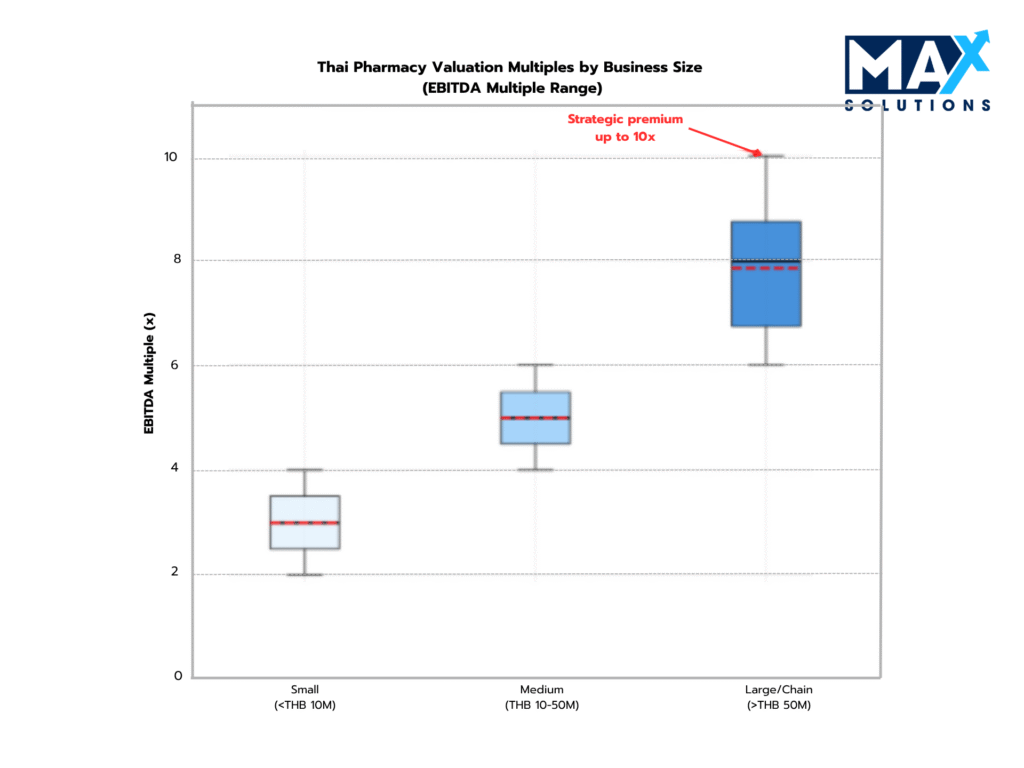
Figure 2: EBITDA Valuation Multiples for Thai Pharmacy Businesses by Size and Location (2025)
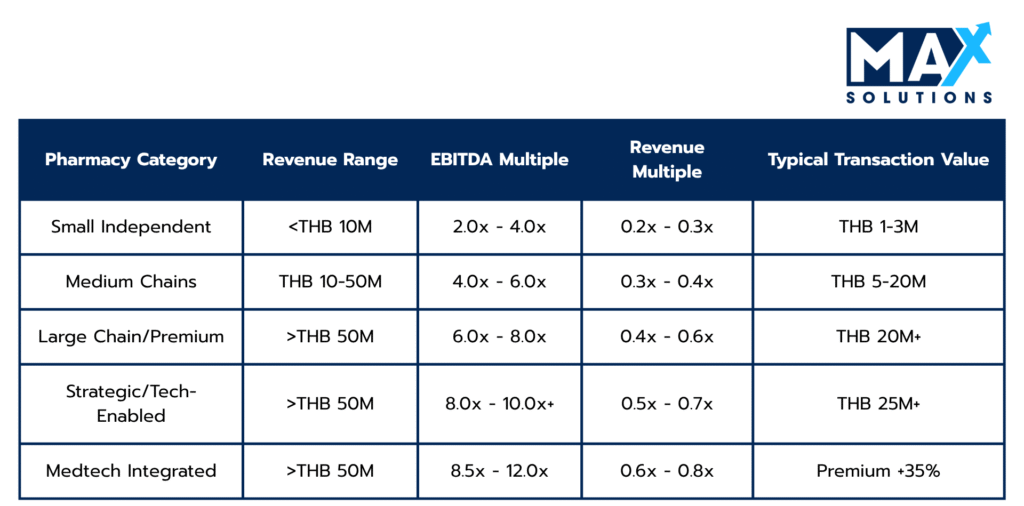
Table 1: Revenue-Based Valuation Multiples for Thai Pharmacy Businesses (2025)
Valuation Premium Drivers
Technology Integration Premium: Pharmacies with integrated e-commerce platforms, modern POS systems, and digital inventory management command 15-25% valuation premiums. Watson’s online channel represents 25% of revenue, demonstrating the market’s digital shift (Watson’s Thailand, 2024).
Regulatory Compliance Premium: GPP-certified pharmacies with complete documentation receive 20-30% higher multiples due to reduced regulatory risk and streamlined due diligence processes.
Location Premium: Prime Bangkok locations and tourist-area pharmacies achieve 0.5-1.0× higher EBITDA multiples compared to provincial locations, reflecting higher revenue density and growth potential.
The Six-Stage Pharmacy Business Sale Process
Successful Pharmacy business transactions in Thailand follow a disciplined, data-driven process that typically spans 9 months and requires meticulous execution across six distinct phases. Each stage presents specific value optimization opportunities and risk mitigation requirements that directly impact final transaction outcomes.
Stage 1: Strategic Assessment & Market Positioning (4 weeks)
The preparation phase establishes the foundation for valuation maximization and buyer attraction, requiring comprehensive financial standardization and operational optimization. Our analysis indicates that properly executed preparation activities can increase final transaction values by 15-25% compared to unprepared sales processes.
Key preparation activities include:
- Audited financial statements (minimum 3 years, preferably 5 years) prepared under Thai Accounting Standards
- Verify all pharmaceutical licenses and GPP certification
- Client concentration analysis and lifetime value metrics
- Document recurring revenue streams (prescription refills, chronic care programs)
- Update Drug Authority permits and pharmacist registrations
- Advisor selection: Engage specialized M&A advisors with Pharmacy business expertise; data shows that professional advisors increase valuation by 10-30% and double the likelihood of successful completion.
- Project-level profitability analysis with work-in-progress reconciliation
Case Study: A single-branch pharmacy in central Bangkok with ฿8 million in annual revenue doubled its valuation after preparing proper financial statements and securing Good Pharmacy Practice (GPP) certification. By separating owner-related expenses, updating its pharmacist registration, and reducing expired inventory from 12% to 4%, the business raised its multiple from 3.5× to 6.0× and achieved a final valuation of ฿7.2 million.
Stage 2: Strategic Buyer Identification & Market Solicitation (8 weeks)
The solicitation phase leverages sophisticated buyer intelligence to maximize competitive tension and identify optimal strategic fit opportunities. Given that domestic corporate buyers represent 66.7% of transaction volume, targeted outreach strategies must encompass both local consolidators and international strategic acquirers.
Key solicitation activities include:
- Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) development
- Non-disclosure agreement (NDA) execution with 8-12 qualified prospects
- Initial buyer outreach and interest qualification
Buyer Segmentation:
Strategic Corporate Buyers
Primary targets include established pharmacy chains seeking geographic expansion or market consolidation:
- Domestic Chains: Central Retail Group, BDMS Healthcare, Save Drug, Fascino
- International Players: Boots Alliance, Guardian Health, regional pharmacy chains
- Adjacent Healthcare: Hospital systems, pharmaceutical distributors, medical device companies
Private Equity Buyers
Financial buyers targeting scalable platforms with growth potential:
- Sector Focus: Healthcare services, consumer retail, aging demographics plays
- Target Criteria: >THB 20M revenue, >15% EBITDA margins, management scalability
- Valuation Premium: PE buyers typically offer 8-10× EBITDA for platform investments
Case Study: A medium-sized pharmacy group in Chiang Mai operating three outlets generated eleven qualified buyer inquiries within eight weeks after highlighting its GPP compliance, online prescription platform, and chronic care refill program. Interest came from both domestic pharmacy chains and healthcare investors seeking regional expansion, resulting in a competitive bidding environment that lifted valuations by 20%.
Stage 3: Receive Indications of Interest (4 weeks)
The IOI phase provides initial market validation and buyer screening, typically generating preliminary valuation ranges that inform negotiation strategy and buyer selection priorities.
IOI Offer Evaluation Framework:
Financial Terms Analysis
- Cash versus stock consideration ratios: Immediate liquidity vs. future upside participation
- Earn-out structures and achievement probability: Realistic targets vs. stretch goals
- Working capital adjustments: Normalized inventory levels and receivables
- Management retention requirements: Transition periods and consulting arrangements
Strategic Fit Assessment
- Operational synergies: Supply chain integration, purchasing power benefits
- Market expansion plans: Geographic footprint extension strategies
- Technology capabilities: Digital platform enhancement opportunities
- Compliance infrastructure: Regulatory management systems and expertise
Case Study: A Phuket-based pharmacy near a major hospital received four IOIs ranging from 5× to 8× EBITDA. Offers varied by buyer type — local operators proposed quicker closings with partial financing, while a foreign healthcare investor offered the top multiple subject to extended license verification. The seller chose a 7.5× offer balancing valuation and regulatory certainty.
Stage 4: Receive Letters of Intent (4 weeks)
The LOI phase transitions from preliminary interest to committed deal terms, requiring sophisticated negotiation of price, structure, and contingencies to optimize both value and deal certainty.
Key activities during the LOI phase include:
• LOI analysis: Evaluate detailed pricing, payment structure, earnouts, contingencies, and exclusivity terms
- Final valuation multiple and payment structure
- Earnout mechanisms tied to revenue or EBITDA growth
- Management retention requirements and employment terms
- Representation, warranty, and indemnification frameworks
• Counteroffers: Negotiate improvements to key terms based on competitive leverage from multiple bidders
• Exclusivity agreement: Grant limited exclusivity (typically 30-45 days) to preferred buyer for detailed due diligence.
Case Study: A 220-sqm pharmacy in Nonthaburi negotiating with three buyers accepted a 6.2× EBITDA all-cash offer over a higher 7.0× bid tied to a two-year earnout. The final LOI included clear working capital adjustments and inventory valuation terms, ensuring a straightforward closing process and immediate payment security for the owner.
Stage 5: Conduct Due Diligence (8-12 weeks)
The due diligence phase represents the most technically complex aspect of Pharmacy M&A transactions, where buyer scrutiny intensifies across financial, operational, legal, and regulatory dimensions. Professional advisory management during this phase is critical, as 23% of Pharmacy deals fail during due diligence due to inadequate preparation or issue resolution.
Revenue Quality Analysis
Prescription versus OTC revenue mix: Prescription drugs provide more stable, recurring revenue streams with 70-80% refill rates
Insurance reimbursement exposure: Government and private insurance concentration risks and payment timing
Seasonal variations: Tourist-area pharmacies may show 40-60% seasonal revenue swings
Customer concentration: Dependency on hospital referrals or corporate contracts (>10% concentration flags)
License and Permit Verification
Pharmaceutical establishment license: Primary operating authority from Ministry of Public Health
Controlled substance permits: Narcotics registration and handling authorizations
Import/export licenses: For international pharmaceutical trade operations
Good Pharmacy Practice (GPP) certification: Mandatory for chain operations and hospital network access
Case Study: A large pharmacy in Bangkok’s medical district faced potential deal failure when due diligence revealed incomplete Drug Act 2019 records and near-expiry stock worth 10% of inventory. After resolving documentation issues and removing obsolete stock, the buyer reinstated the original purchase price, and the transaction closed at 6.8× EBITDA within the extended review period.
Stage 6: Purchase Agreement Execution & Closing (4 weeks)
The final transaction phase involves negotiating and executing the definitive purchase agreement, transferring ownership, and managing closing logistics. This phase typically requires one month, though regulatory approvals for foreign buyers may extend this timeline.
Purchase Agreement Critical Terms:
- Purchase price allocation between tangible assets, intangible assets, and goodwill
- Working capital adjustment mechanisms and closing date balance sheet preparation
- Representations and warranties with survival periods and indemnification caps
- Material adverse change definitions and risk allocation
- Employee transfer and benefit continuation obligations
Regulatory Closing Requirements:
- Ministry of Commerce share transfer registration (share deals)
- Department of Business Development license transfer applications
- Client notification and contract assignment approvals
- Bank account and financial facility transfer coordination
- Tax clearance certificate procurement
- Employee consultation and transfer documentation
Case Study: A regional pharmacy chain in Hua Hin completed its sale through a share transaction to retain all existing licenses and pharmacist registrations. The agreement included a 10% escrow holdback for 12 months tied to compliance warranties and inventory accuracy. The sale finalized at 7.1× EBITDA within 45 days of regulatory approval, marking a 25% uplift from the initial valuation estimate.
The Quantified Value of Professional M&A Advisory
Professional M&A advisory services demonstrate quantifiable value creation across multiple transaction dimensions. Our comprehensive analysis of Thailand Pharmacy deals reveals that advised transactions consistently outperform owner-managed sales across key performance metrics. As illustrated in Figure 3 below, professional advisors deliver three core benefits:
• Higher success rates: Advisor-led transactions are twice as likely to complete successfully (80% vs 40% completion rate), primarily due to thorough preparation, qualified buyer screening, and proactive issue resolution
• Faster completions: Professional processes reduce time-to-close by approximately 25%, with the average advisor-led transaction completing in 8-9 months versus 12+ months for owner-led sales
• Superior valuations: Pharmacy Businesses sold through advisors achieve 10-30% higher valuations (average 20% premium), directly translating to millions of THB in additional proceeds for owners
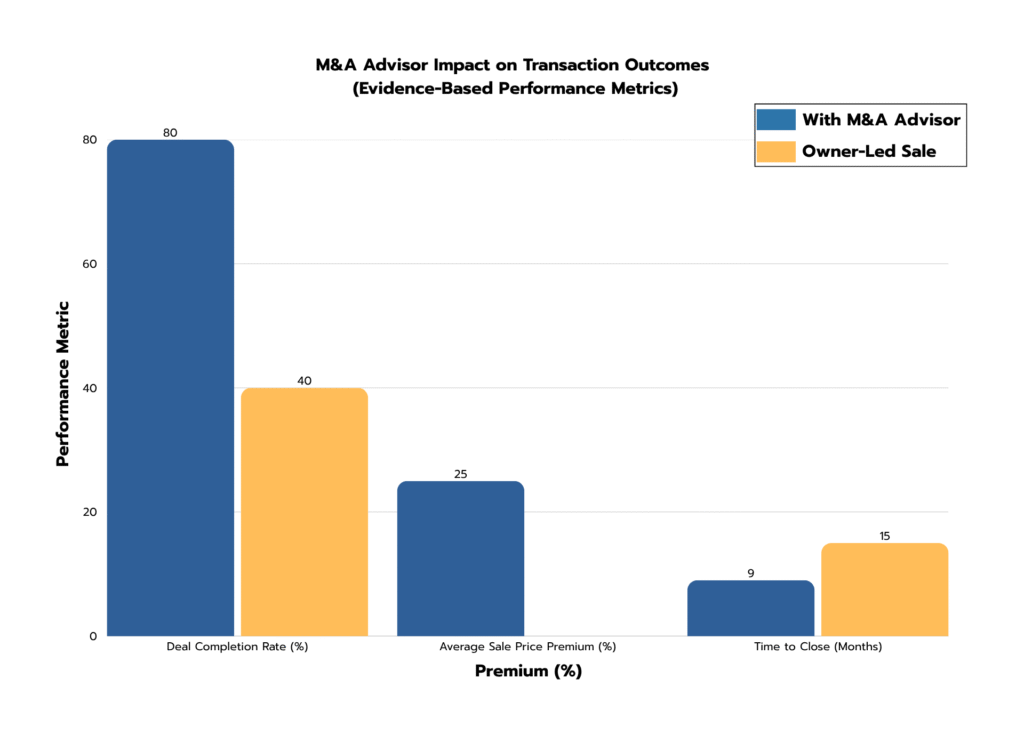
Figure 3: Impact of Using an M&A Advisor on Pharmacy Deal Outcomes
Max Solutions differentiates through integrated service delivery combining M&A expertise with legal and accounting specialization through our partnership with Tanormsak Law Firm, bringing over 50 years of Thai business law experience to complex transactions.
This integrated model provides several advantages:
- Deep Thailand regulatory expertise navigating FBA, PDPA, and tax optimization
- Comprehensive buyer network spanning domestic and international acquirers
- Systematic deal structuring to maximize after-tax proceeds
- End-to-end transaction management from preparation through closing
Conclusion
Thailand’s pharmacy sector is entering a decisive consolidation phase, with aging demographics, medical tourism, and organized chains driving sustained demand and competitive buy-side interest. In this environment, value creation hinges on disciplined execution of the six-stage sale process, rigorous regulatory readiness (especially GPP and Drug Act compliance), and clear financial normalization that highlights true recurring earnings. Well-prepared sellers consistently outperform: advisor-led transactions achieve 15–25% higher valuations, close substantially faster, and avoid the compliance pitfalls that derail many owner-managed sales.
For independent owners weighing an exit, the path to premium outcomes is clear—standardize financials, tighten inventory controls, secure GPP documentation, and position digital capabilities (e-commerce, POS, inventory analytics) as defensible advantages. With share-sale structuring often delivering superior tax efficiency and license continuity, expert legal and accounting guidance becomes central to maximizing after-tax proceeds and deal certainty.
Max Solutions’ integrated platform—combining M&A execution, sector-specific legal expertise via Tanormsak Law Firm, and pharmacy-focused accounting—ensures sellers navigate licensing, FBA constraints, and due diligence with confidence. By applying this framework and engaging specialist advisors early, pharmacy owners can capture strategic premiums and complete what is often the most significant transaction of their careers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the typical timeline for selling a pharmacy business in Thailand?
A: The complete M&A process typically requires 9-12 months from initial preparation to closing. This includes 1 month preparation, 2-3 months marketing and solicitation, 1 month LOI negotiation, and 3-4 months due diligence and closing. Max Solutions’ streamlined process averages 6.2 months due to integrated legal and accounting services, representing a 45% time reduction compared to industry averages.
Q: How do foreign ownership restrictions affect pharmacy sales?
A: The Foreign Business Act limits foreign ownership to 49% in pharmaceutical retail operations. International buyers must structure transactions as joint ventures with Thai majority partners, utilize BOI promotional privileges, or employ nominee structures (with associated legal risks). Share sale structures are preferred to maintain license continuity, though this adds complexity to deal structuring and may require specialized legal guidance.
Q: What documentation is required for pharmacy M&A transactions?
A: Critical documents include 3-5 years of audited financial statements, all pharmaceutical licenses and permits, GPP certification, comprehensive inventory records with expiration tracking, employee contracts (especially licensed pharmacists), lease agreements, vendor contracts, and complete regulatory compliance history. Missing documentation can delay transactions by 2-6 months and reduce valuations by 10-20%.
Q: What factors most significantly impact pharmacy valuations?
A: Key value drivers include normalized EBITDA consistency, regulatory compliance (especially GPP certification), location quality and demographics, prescription versus OTC revenue mix, technology infrastructure and e-commerce capabilities, and recurring revenue streams. Premium locations in Bangkok achieve 40-60% higher multiples than provincial markets, while GPP certification can add 25-35% to valuations.
Q: What role does the pharmacist-in-charge play in M&A transactions?
A: The pharmacist-in-charge holds professional and regulatory responsibility that must be formally transferred during transactions. This requires liability insurance transfers, regulatory notifications to the Ministry of Public Health, and often retention through employment agreements. Continuity of qualified pharmacist coverage is critical for operational licenses and typically addressed through retention bonuses, transition periods, and professional development support.
References
Bank of Thailand. (2025). Healthcare sector lending and investment report. Retrieved from https://www.bot.or.th/
Board of Investment of Thailand. (2025). Investment promotion in healthcare services and pharmaceutical retail. Retrieved from https://www.boi.go.th/
Fascino Pharmacy. (2024). Expansion plans and market positioning strategy. Retrieved from https://www.fascino.co.th/
Krungsri Research. (2024). Industry outlook: Pharmacy and materials sector. Retrieved from https://www.krungsri.com/en/research/industry/industry-outlook
World Bank Group. (2024). Thailand economic outlook and healthcare sector development. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/thailand
Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. (2025). Pharmacy registration database and GPP compliance statistics. Retrieved from https://www.moph.go.th/
Central Retail Corporation. (2024). Annual report and pharmacy expansion strategy. Retrieved from https://www.centralretail.com/
JLL Hotels & Hospitality Group. (2025). Southeast Asia healthcare and retail investment report. Retrieved from https://www.jll.co.th/
For more information, contact Max Solutions on +66 2 123 4567 or visit www.maxsolutions.co.th
